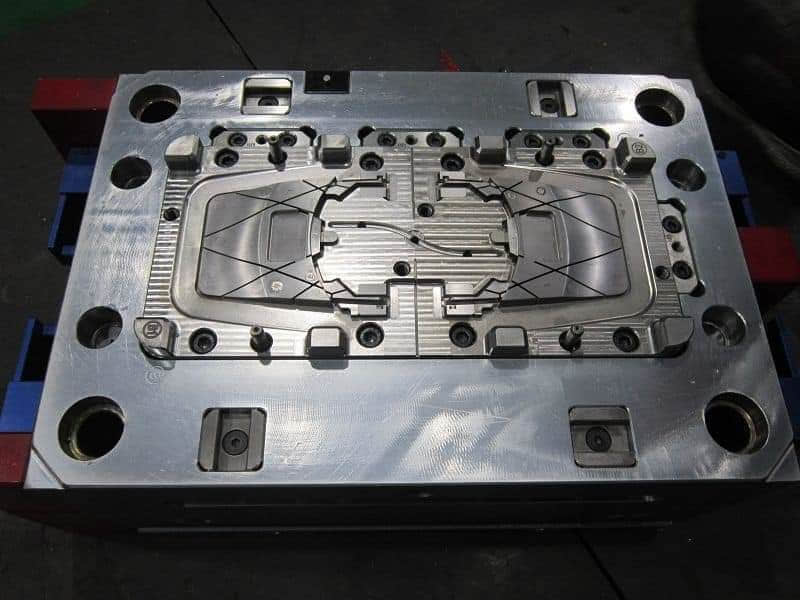
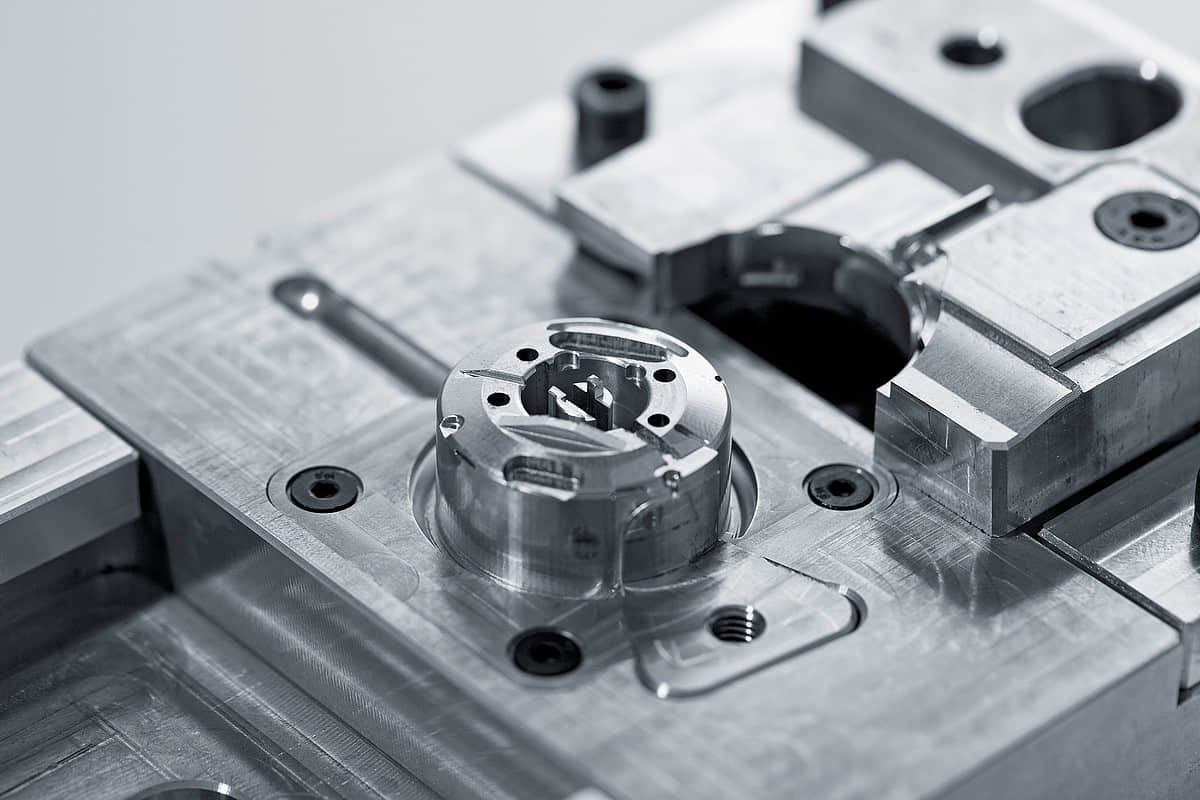


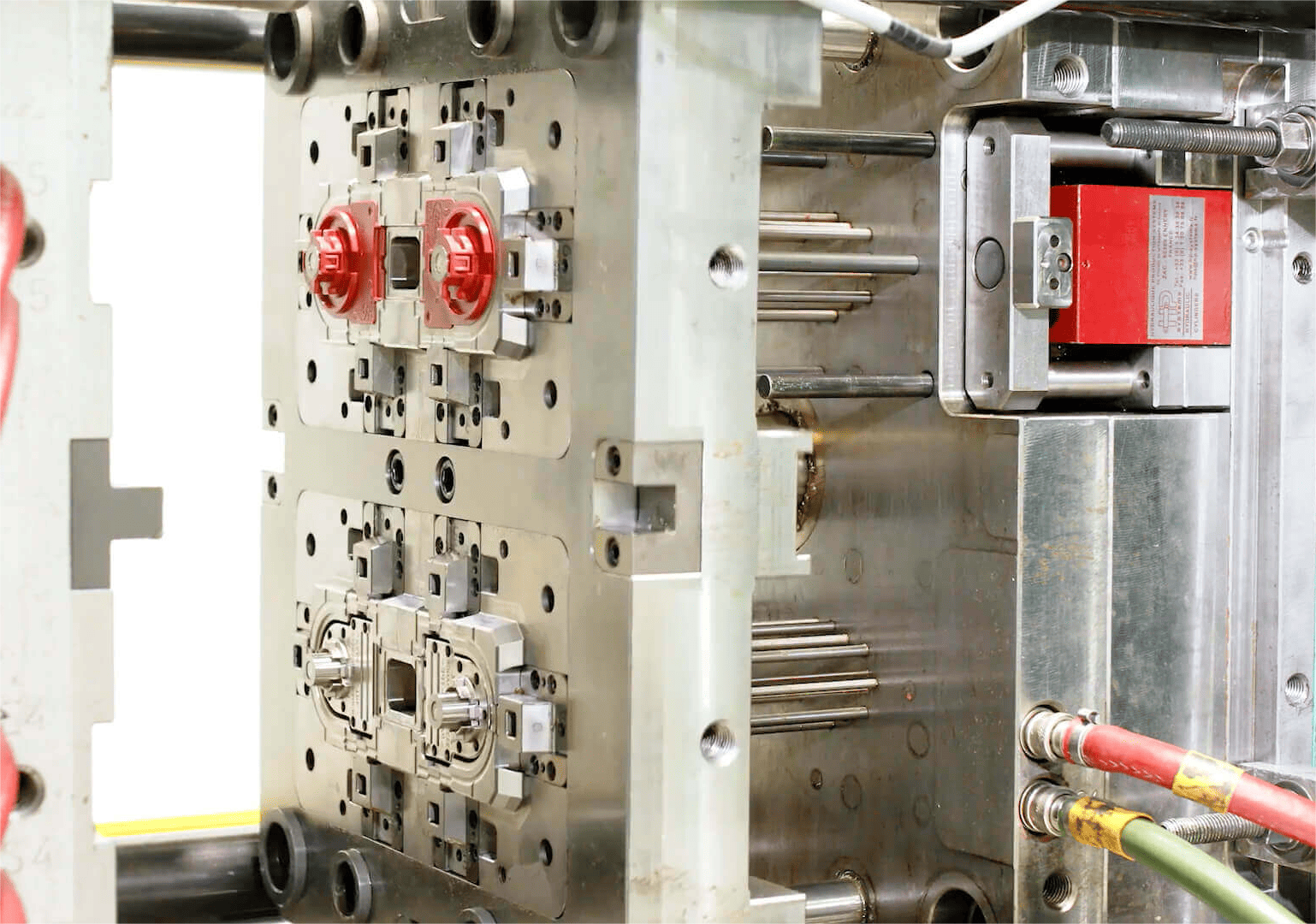


Yes, the material chosen for the injection mold significantly impacts the quality of plastic parts. Attributes like heat transfer rate, hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the mold material directly determine consistency in dimensional tolerances, surface finish and conformity to specifications for molded components.
45 # Tool steel is typical choices for mold bases due to their strength, hardness and corrosion resistance properties.
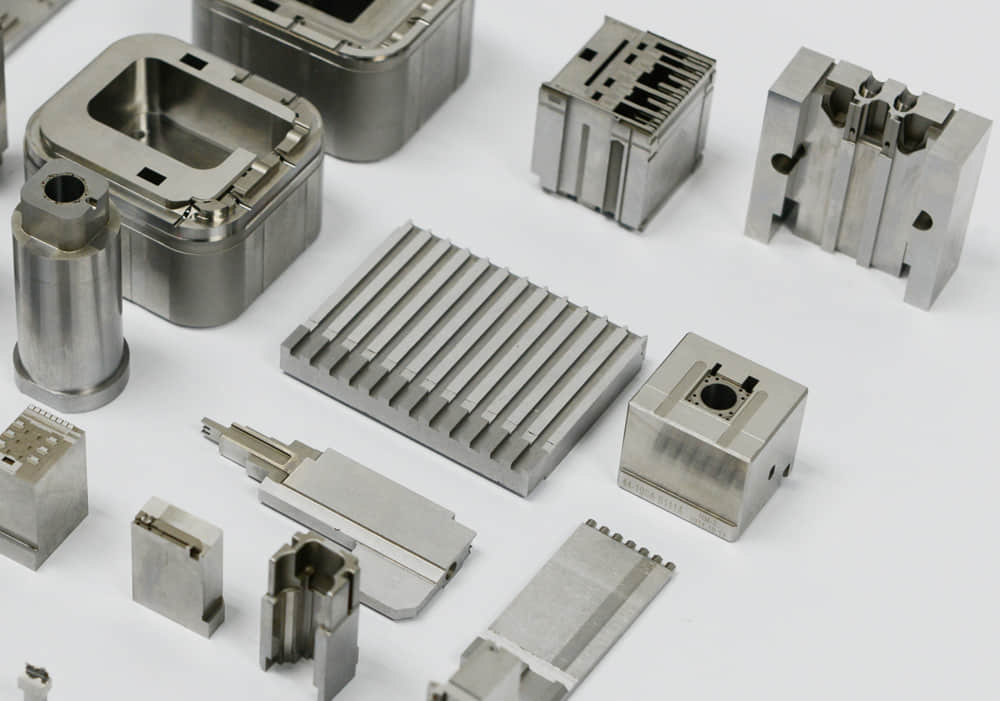
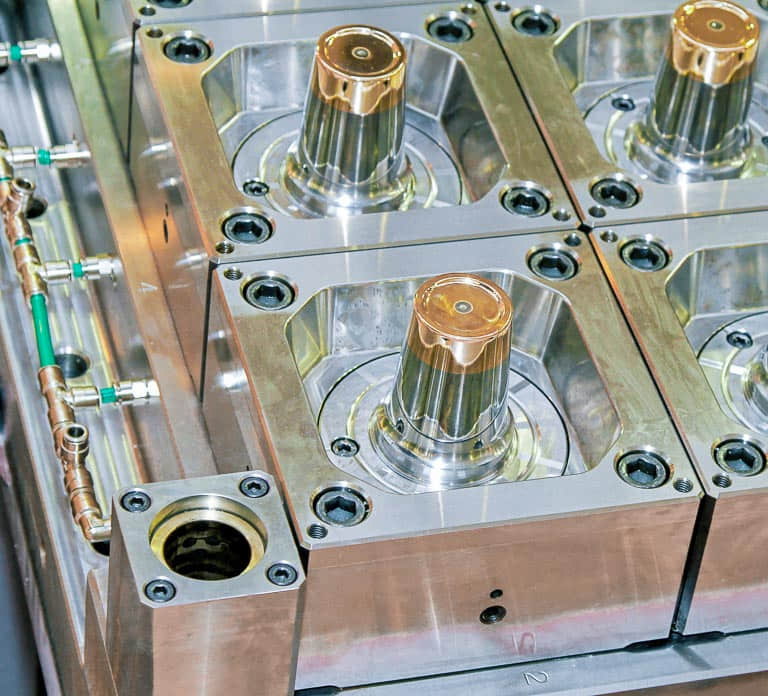
Cavity and core blocks require high hardness above 48HRC for wear resistance as well as good thermal conductivity to facilitate rapid cooling. Materials like P20 or SCM420 stainess steel are suited.
Sliders, lifters, and other movable mold components are wear-prone parts. When selecting injection tooling materials, hardness and toughness should be considered. Using hardened tooling steel can prevent wear, thereby maintaining strict tolerances during long-term production operation. For high-volume injection molds, S136 mold steel can be considered, for medium and low-volume molds, 2738 and 718H can be considered.
Aluminum is an economical choice for prototypes or low-volume tooling. However, its softness limits use to small runs with non-abrasive plastic materials.
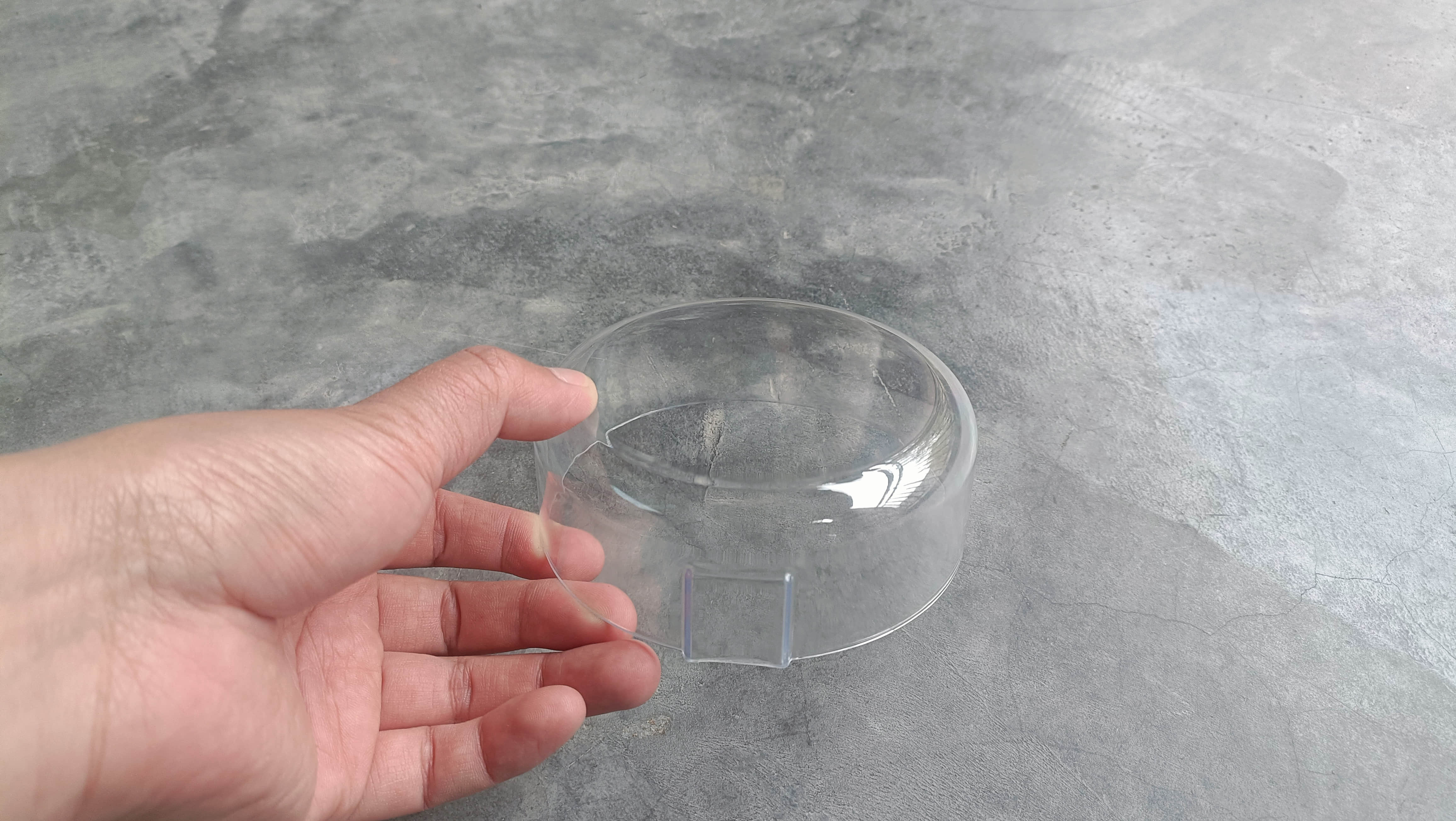
Electroplating chromium on the cavities of plastic molds can prevent corrosion and prolong the service life of molds, especially for molds used with abrasive injection resins such as PFA and PVC. It can also improve the overall smoothness, reduce scratches, and improve quality, especially for transparent molded parts made of materials like polycarbonate and Nylon 10.