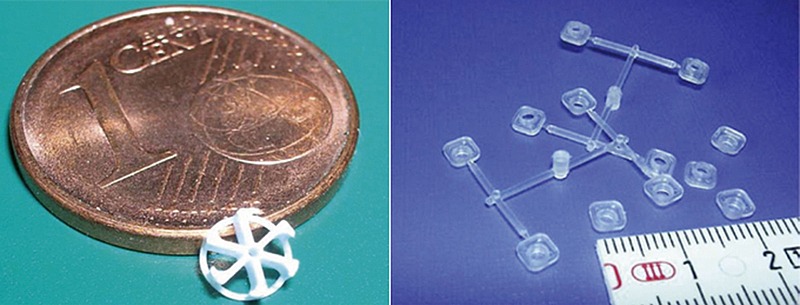
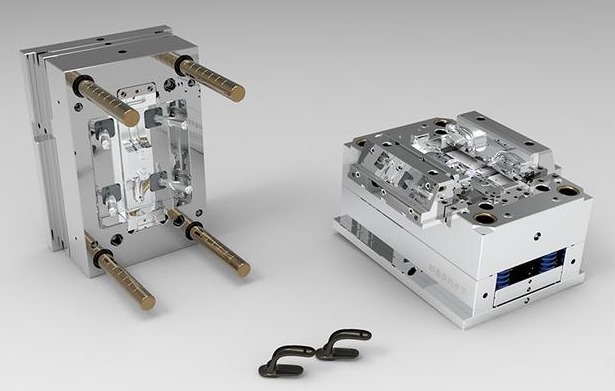

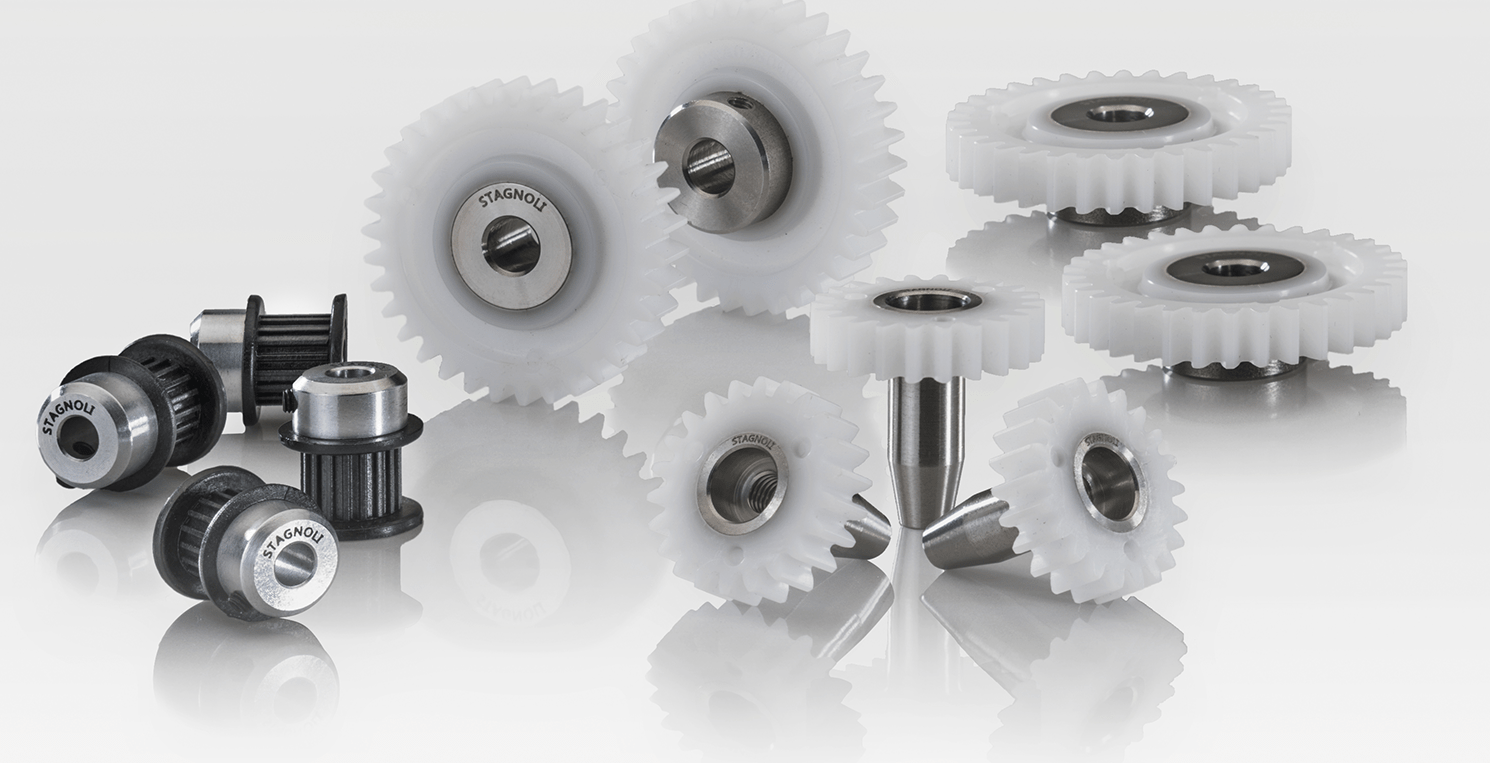





PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) is a kind of high performance engineering plastic with excellent performance, which is widely used in many fields such as automobile, electronic and electrical, mechanical manufacturing and so on. This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the characteristics, applications and processing processes of PPS plastics to better help engineers and designers to provide a detailed reference when selecting high performance plastics.
PPS stands for polyphenylene sulfide, which is a thermoplastic resin with sulfide groups in the molecular main chain. It is a crystalline polymer.
Its glass transition temperature is 150℃ and melting point is 281℃. PPS has excellent heat resistance, corrosion resistance, radiation resistance, flame retardance, balanced physical and mechanical properties and excellent dimensional stability as well as good electrical properties. It is widely used as a high-performance polymeric structural material and through filling and modification, widely used as an engineering plastic. Meanwhile, it can also be made into various functional films, coatings and composites, and has achieved successful applications in electronics, aerospace, automotive transportation and other fields.

PPS was first confirmed to exist by scientists Freidel and Craft in 1888.
In 1968, Dr. H. Wayne Hill Jr. and James T. Edmonds of Phillips Petroleum Company developed and marketed “Ryton® PPS” by successfully developing a method of manufacturing polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) via solution polycondensation of dichlorobenzene and sodium sulfide in the polar organic solvent N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). This marked the starting point of industrial PPS production. With industrial production achieved in 1973, PPS began to find applications in global markets.
In 1984, Macallum first successfully synthesized PPS via a melted reaction of dichlorobenzene, sodium carbonate and sulfur yellow in the laboratory, opening up a new pathway for PPS production.

In 1985, related PPS patents expired, leading many companies to enter the PPS production field. Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals developed linear PPS under the brand name “Fortron” PPS using new technology, which was the second-generation high molecular weight linear PPS resin with superior performance. Thereafter, with continuous technological advances, the maturity of PPS synthesis production technology enabled many companies such as DIC, Toyobo and Tosoh to establish their own PPS synthesis production lines. This intensified market competition while also promoting rapid development of PPS technology and markets.
In the 21st century, China’s PPS industry also achieved rapid development. Industrial PPS production was realized in China in 2001 and grew quickly over the following decade. Currently, China has huge demands for PPS resins and modified composite materials, making it an important player in the global PPS industry.
The molecular structure of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is formed by the alternating arrangement of benzene rings and sulfur atoms, resulting in stable chemical bonds and high polymeric stability.

The PPS main chain is composed of benzene rings and sulfur atoms connected by sulfur atoms. The sulfur atoms in the PPS main chain are not fully saturated and can form conjugated structures with adjacent benzene rings. Through oxidation, the sulfur atoms can form sulfone or sulfate structures, or the benzene rings and adjacent large molecules can form oxidative bridges or crosslinking without breaking the main chain. This results in PPS’s exceptional heat oxidation stability with a maximum continuous use temperature of 260°C and thermal decomposition temperature of 522°C.
The rigid benzene rings give PPS a high degree of crystallinity and corrosion resistance, while the flexible sulfide bonds contain sulfur atoms that impart flame retardancy without the need to add flame retardants to achieve a V0 flame retardance rating.
The molecular structure of PPS also determines its characteristics such as extremely low water absorption, mechanically properties that can be improved through reinforcement modification, outstanding thermal properties and prominent electrical properties.

This is the most basic type of PPS, which is a linear polymer that is white or light yellow in color, with a medium molecular weight and generally average mechanical strength. It will crystallize rapidly when heated above its glass transition temperature.
This PPS has a higher molecular weight than conventional PPS and is usually used to produce thin films and coatings. It has superior mechanical properties due to the higher molecular weight.
The mechanical strength and heat resistance of PPS are increased by adding glass fibers, commonly used for structural components requiring high performance.
Adding carbon fibers can further enhance the mechanical properties of PPS and is suitable for high-end application fields.
Using inorganic materials such as calcium carbonate and talc powder to improve the abrasion resistance of PPS and reduce costs.
Adding minerals such as wollastonite and muscovite to improve the dimensional stability and heat resistance of PPS.
Altering the molecular structure of PPS through chemical methods to improve its toughness, processability or other specific properties.
Blending with other plastics such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to achieve better integrated performance.
Adding conductive materials such as carbon black makes PPS electrically conductive and suitable for electrostatic discharge or electromagnetic shielding applications.
Adding antistatic agents for use in electronic products requiring antistatic performance.
Modified PPS is to compound or dope PPS with other thermoplastics or various reinforcing materials (glass fiber, carbon fiber, etc.) to further improve the performance of PPS, like mechanical strength, rigidity, heat resistance, etc.
The excellent physical properties of PPS plastic make it an ideal material choice for high-temperature, high-load, and high-chemical corrosion environments. The specific physical property data may vary depending on the PPS manufacturer, grade and test conditions.

Density: The density of PPS plastic is around in the range of 1.34-1.45 g/cm³. PPS grades commonly used in applications are often modified, such as glass fiber reinforced, inorganic filled and carbon fiber reinforced, which will increase the density, generally density of PPS glass filled plastic reaching 1.60-1.68 g/cm³.
Shrinkage rate: The shrinkage rate of PPS plastic material is relatively low, generally between 0.3-0.8%. The relatively low shrinkage rate is conducive to ensuring dimensional stability of products during injection molding processes. The specific shrinkage rate data may vary according to processing conditions and product shapes.
Melt flow rate (MFR): The melt flow rate of PPS varies depending on the specific grade but is generally within the range of 1-30 g/10min.
Glass transition temperature (Tg): The Tg of PPS is approximately between 85°C to 100°C.
Melting point (Tm): The Tm of PPS is typically around 280°C. These high heat properties allow PPS plastic to maintain stable physical properties at high temperatures and are suitable for various high-temperature applications.
Heat deflection temperature (HDT): The HDT of PPS is approximately between 200°C to 220°C.
Continuous use temperature: PPS can be used long-term between 200°C to 220°C.
PPS plastic Hardness: PPS plasitc is so hard that tapping on a PPS plastic product sounds like tapping iron.The Rockwell hardness (HRR) of PPS is typically around 120 HRR.
Tensile strength: The tensile strength of PPS is approximately 60-80 MPa.
Elongation at break: The elongation at break of PPS is generally between 2-5%.
Impact strength: The notched impact strength of PPS at room temperature is approximately 10 kJ/m².
Dielectric constant: The dielectric constant of PPS at 1 kHz is approximately 3.5.
Volume resistivity: The volume resistivity of PPS is very high, up to 10^16 Ω·cm.
Water absorption: PPS has an extremely low absorption rate, almost non-absorbent, which is convenient for PPS injection molding.
Chemical resistance: PPS has excellent chemical resistance to most inorganic acids, alkalis and salts, but may react to some strong oxidizing agents and organic solvents.
Flame retardancy: PPS has good flame retardancy and can achieve a UL94 V-0 rating. This characteristic makes it commonly used for electrical housing products.
PPS has outstanding properties:
PPS plastic prices are mainly affected by the following factors:
the main raw materials of PPS include p-dichlorobenzene and sodium sulfide, the price fluctuations of these raw materials directly determine the price of PPS plastic.
PPS production process is complex, requires high temperature and high pressure conditions, energy prices, labor costs, etc. will affect the price of PPS.
in recent years PPS in the automotive, electrical and electronic, aerospace, machinery and many other industries are widely used, will also affect the final price of PPS plastic.
China’s PPS production line construction progress, but the capacity is still insufficient to fully meet market demand, resulting in price increases. China’s PPS industry average price overall showing a downward trend, the average sales price of PPS in 2023 is about 6428 dollars / ton.
We summarize the key brands PPS price overview:
Toray (Japan): as a leading brand in the PPS industry, the price of its products is usually higher. Roughly $ 20 to $ 40 per kilogram.
Tecna (US): also a well-known brand in the field of PPS, its product prices are also more stable. About 18 ~ 35 U.S. dollars per kilogram.
Poly (Japan) : Poly’s PPS plastic enjoy a good reputation in the market, the price is relatively high but stable performance. Price per kilogram 22 ~ 42 U.S. dollars.
China brand PPS: The price of Chinese brand PPS is US$10~25 per kilogram. Although the overall price is low, its performance is comparable to that of the big international brands of PPS plastics.
Polyphenylene sulfide, as a high-performance engineering plastic, can be molded through various processing techniques including injection molding, extrusion molding, compression molding and thermoforming. Different molding methods are suitable for different product requirements and the appropriate process should be selected based on specific conditions. During processing, it is also important to ensure adequate drying and temperature control of PPS to ensure the performance and quality of molded parts. Here are 10 common molding processes for PPS plastic summarized:
Injection molding is one of the most common and widely used methods for processing PPS plastic, suitable for producing complex shaped and precisely dimensioned parts. PPS has a relatively high melting temperature (about 300-330°C) requiring specialized high-temperature injection molding machines. The injection process requires sufficient PPS drying to prevent bubbles and flow problems caused by moisture. Temperature, pressure, holding pressure time and other parameters also need to be controlled to ensure dimensional accuracy and stable performance of molded parts. Injection molding has advantages of high production efficiency and stable part quality but high mold cost and unsuitability for small batch production.

PPS plastic can also be manufactured into various profiles such as pipes and boards through extrusion. The high melt viscosity of PPS requires extrusion equipment with good mixing ability and high extrusion pressure. Temperature control is important during extrusion to ensure flowability and stability of the PPS melt. Proper cooling and post-processing of extruded products is also needed to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Extrusion molding has advantages of high efficiency and low cost, suitable for mass production.
Compression molding of PPS plastic is mainly used to produce large PPS plastic products. In the compression process, preheated and softened PPS is placed in a mold and formed through applied pressure and temperature. Compression molding can produce complex and large-sized products but has relatively low production efficiency.
PPS can also be processed into various thin-walled products such as films and sheets through thermoforming. This method is suitable for producing some large-area, thin-walled plastic products. In the PPS thermoforming process, the PPS plastic sheet is heated to a softened state and then formed to the shape of the mold cavity by pressure to form the desired PPS plastic product. Proper preheating and molding of the PPS plastic sheet material is needed to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the product.
Transfer Molding is a method suitable for producing PPS plastic parts with fine threads or complex shapes. It works by placing the PPS material on one side of the mold and molding plastic part through pressure flowing to the other side of the mold.
PPS plastic can also be processed by powder metallurgy, i.e. making PPS resin into powder and then molding it through pressing and sintering, suitable for producing high-density and high-strength PPS parts.
Sprayis a processing method that involves spraying PPS powder onto a substrate through a spray gun and then curing it through heating to form a coating. This method is suitable for surface modification and protection of the substrate to improve properties such as abrasion and corrosion resistance. Spray forming has advantages of simple operation and uniform coating but production efficiency is limited by spray equipment and techniques.
PPS can be laminated with other materials (glass fiber and carbon fiber) through composite molding to enhance its mechanical and heat resistance properties.
With the development of 3D printing technology, PPS is also used as a 3D printing material, especially selective laser sintering (SLS) which can print complex geometries.
PPS plastic rod and PPS plastic sheet can also undergo post-processing like turning, milling, drilling by CNC machining to meet specific dimensional and shape requirements of parts.

We have collected and summarized some typical PPS plastic manufacturers around the world to better help you choose the correct PPS plastic raw material supplier. Each PPS manufacturer has its own characteristics, you can compare and carefully identify them.
Toray is one of the largest PPS resin manufacturers globally, renowned for its TORELINATM PPS resin brand, which has widespread applications in automotive, electronics/electrical components, water-related parts, etc. due to its outstanding heat resistance, dimensional stability and chemical stability.
Ticona is a subsidiary of Celanese and a global leader in producing engineering polymers including PPS. They offer a diverse portfolio of customized PPS grades tailored for different industries and applications.
Solvay is a global chemicals company that produces various high performance plastics including Ryton® PPS and PEEK resins, which are favored in multiple industries for their heat and chemical resistance. They are renowned for their expertise in developing high-performance PPS compounds for demanding applications.
DIC produces various plastics and resins including PPS resin, developing innovative PPS compounding and polymerization technologies enabling the production of PPS plastics with outstanding characteristics.
Celanese offers various engineering plastics including PPS, which are used in harsh application environments due to their high performance properties.
SK is a Korean chemicals company producing various high performance plastic resins including PPS, which have important uses in the electronics and automotive industries.
Tosoh is a Japanese chemicals and healthcare company producing various high performance resins including PPS, renowned for its commitment to quality and innovation in the PPS market.
Toyobo is an integrated Japanese company involved in textiles, chemicals and healthcare among other areas, offering various engineering plastics including PPS.
Zhejiang NHU Co., Ltd. is a renowned PPS plastic manufacturer in China, providing specialty engineering plastics including PPS resin and dedicated to R&D, modification and production of PPS.
Designing PPS plastic parts is a complex and delicate process that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors such as material properties, processing characteristics and part usage environment. Through scientific design and optimization, PPS parts can perform excellently in actual applications to meet various complex and stringent demands. Here are some considerations for PPS plastic part design summarized based on our 20 years of molding experience:

PPS plastic has excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance and mechanical properties making it very suitable for environments requiring high temperatures, chemical corrosion and mechanical stresses. Material grade selection should fully utilize these PPS advantages.
PPS can be molded through processes like injection molding, extrusion, compression molding. Process characteristics should be considered in design, e.g injection requires temperature and pressure control, extrusion needs flowability and dimensional accuracy attention. Subsequent processes like thermoforming, welding should also be considered.
High melting point of PPS requires specialized equipment and process parameters like high molding temperature and mold temperature. Equipment selection should be planned beforehand in design to avoid late modifications and increased costs.
Higher PPS molding temperature requires considering material flow and fusion properties in mold design. Mold temperature selection is critical to ensure part quality and dimensional accuracy. Mold material selection should also consider PPS processing characteristics like abrasion resistance and hardness to ensure mold service life and part consistency. Based on our over 10 years of PPS injection molding experience, mold steels like S136, M316 should be selected.
PPS is a crystalline resin with significant shrinkage during molding requiring proper shrinkage allowance design to ensure part dimension accuracy. Shrinkage rates may also differ in flow and vertical directions requiring precise calculation and adjustment in design, and shrinkage varies with mold temperature. Factors must be considered. Different PPS types have different shrinkage rates and glass fiber filled PPS plastic shrinks less than pure PPS.
Dimensional tolerance of PPS parts should be reasonably designed according to application. generally, PPS can achieve high dimensional accuracy but material shrinkage, process influence factors should also be considered. PPS plastic parts tolerances should balance product performance, appearance and cost.
PPS part wall thicknesses should be uniform to reduce uneven shrinkage and stress concentration during molding.
PPS mechanical properties like tensile strength, impact resistance should be considered. Stress concentrations at sharp corners, holes should adopt radiused designs to reduce stress concentration. Assembly, joining factors should also be considered to select suitable connection methods.
PPS plastic part design should consider cost effectiveness, optimizing design to reduce material and processing costs while maintaining structural integrity.
Considering PPS thermal expansion characteristics, suitable assembly methods like elastic connections or clearance allowances should be selected.
Long term working temperature range of the PPS part usage environment should be considered to ensure properties remain stable within specifications. Typical long term working temperatures for PPS products is 180-220°C and actual applications should ensure operation within this range.
If PPS part will contact specific chemicals, its resistance to these chemicals should be evaluated in design.
PPS has relatively weak impact resistance requiring reinforcement considerations like adding ribs or glass fiber filled PPS.
Lower PPS CTE nearing some metals requires considering problems from CTE mismatches with other materials in design.
PPS is UV sensitive, long exposure may lead to property deterioration. Design should consider UV exposure environment and include UV protection if needed.
PPS parts may require post processing like annealing to relieve internal stresses. Design should consider processing influence on dimensions and properties.
We have summarized some typical applications of PPS plastic based on our more than 10 years of PPS plastic molding experience.
Engine components in automobiles requiring heat and chemical resistance include typical ignition system components, heaters, exhaust system assemblies, sensors and fuel system parts. PPS parts are critically important for improving the reliability and durability of automotive components.

The excellent electrical insulation properties of PPS resin make it an ideal material for manufacturing electronic and electrical components such as circuit boards, connectors, capacitor insulation parts and heat dissipation sheets. In addition, PPS can withstand high temperatures during soldering processes and is often used in electronic assemblies using surface mount technology (SMT) processes.
Properties of PPS such as light weight, high strength and heat resistance make it suitable for manufacturing internal components of aircraft, thermal protection systems for spacecraft and aircraft engine parts. Typical applications include corrosion and abrasion resistant parts for ships and submarines, aircraft plug-in components, coil frames requiring the material to maintain properties under extreme environments.
The chemical corrosion resistance of PPS makes it suitable for the manufacture of equipment such as pumps, valves, pipes and reactors in the chemical industry. These components are often exposed to corrosive chemicals and the use of PPS prolongs the service life and safety of the equipment.
PPS is widely used in the manufacture of mechanical parts like pump casings, pump impellers, gears, pulleys, universal joints, seals, flanges, counters, levels, flowmeters, bearing holder frames, etc.
PPS can be used to manufacture parts for water treatment equipment such as filtration materials, pump impellers and housings because of its resistance to hydrolysis and common disinfectants.
Biocompatibility and disinfectant resistance properties of PPS make it suitable for medical devices including surgical tools, diagnostic equipment, drug delivery devices, surgical probes, filtration systems, surgical tools and endoscopes.

In the consumer products sector, PPS plastic material is used to manufacture high-performance pot handles, microwave components, iron parts and hair dryer components requiring heat resistance.
Radiation resistance enables PPS to be used in some key components in the nuclear industry such as seals for nuclear reactors and certain non-active components and protective materials.
PPS is used for heat sinks and reflectors in LED lighting devices, helping to improve LED light output efficiency and stability due to its good thermal conductivity and heat resistance.
PPS is also a material used in the 3D printing field, especially in applications requiring heat and chemical corrosion resistance.
As a high-performance engineering plastic, polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) plastic is favored in industrial applications for its excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, mechanical strength and electrical insulation. It is suitable for high temperature and high corrosion applications. sexual environment. However, PPS also has certain limitations, such as relatively high processing costs and the processing process may require special equipment and processes, which limits its use in certain specific application scenarios. Nevertheless, the comprehensive properties of PPS make it still an important material choice in many fields with high performance requirements. Below we will discuss the characteristics of PPS and better help you understand PPS plastic.
Outstanding heat resistance
PPS plastic material can be used continuously at temperatures between 200°C to 220°C for a long time without affecting physical properties. It can withstand even higher temperatures for short periods, making it suitable for high temperature working environments.
Excellent chemical resistance
PPS has very good corrosion resistance to most acids, alkalis, salts and organic solvents, allowing PPS parts to work stably in harsh chemical environments.
Good mechanical properties
PPS has high strength, high rigidity, high toughness and good creep resistance properties, maintaining its shape without deforming or breaking under continuous external loads.
Excellent electrical insulation
PPS can maintain good electrical insulation properties even in high temperature and humid environments, suitable for electronic and electrical fields.
Low friction coefficient, high wear resistance
PPS plastic material have an extremely low coefficient of friction and good abrasion resistance. It is suitable for manufacturing bearings, gears and other motion parts that require abrasion resistance and a low coefficient of friction.
Low smoke toxicity
PPS produces little smoke and releases few toxic gases when burned, suitable for applications requiring high safety.
Resistance to hydrolysis and radiation
PPS is stable in hydrolysis and radiation environments, suitable for special fields such as water treatment and nuclear industries.
Various molding processes
PPS plastics can be manufactured through various processing technologies with injection molding, extrusion molding.
High dimensional stability
PPS has a low coefficient of thermal expansion and low shrinkage rate, close to metals, which is conducive to ensuring the precision and stability of PPS plastic products.
Recyclability
PPS materials can be recycled, benefiting environmental protection and cost control.
Outstanding flame retardancy
It has a self-extinguishing property and can self-extinguish when ignited, reducing fire risk. It can achieve UL 94-V0 by default.
Low water absorption
It absorbs little moisture and has little impact on material properties, maintaining stable performance.

High Cost
PPS plastic cost is relatively high, which limits its widespread use in cost-sensitive applications. The high cost of PPS may limit budgets for some projects compared to more economical plastic materials.
Processing difficulty
The high melting point of PPS results in high processing temperatures as well, requiring special processing equipment and techniques, increasing complexity and cost.
UV light sensitivity
PPS material may degrade after long-term exposure to UV light, leading to performance deterioration. Therefore, it may not be suitable for long-term outdoor use or applications requiring good weather resistance.
Higher brittleness
PPS plastics have higher rigidity and strength but poorer impact resistance, and are more likely to experience brittle fractures under low-temperature environments. This may limit their use in some applications requiring good impact toughness. The statement aims to directly translate the original content into English without any changes in meaning or additions. Grammar and style are considered to maintain accuracy.
Molding shrinkage ratio
The molding shrinkage ratio of PPS material is relatively large, which may result in poorer dimensional stability of molded parts, increasing the difficulty of subsequent processing and assembly.
Melt viscosity
PPS has high melt viscosity, which may cause poorer flowability during processing such as injection molding, posing higher requirements for mold design and processing techniques.
Relatively high processing temperature
The processing temperature of PPS plastics is generally around 300°C, increasing production costs while also limiting available processing techniques.
Limited color options
PPS plastics usually have limited color options and are difficult to color using conventional colorants, limiting its use in applications with special color requirements.
Coefficient of thermal expansion
While the low coefficient of thermal expansion of PPS is an advantage, it may cause thermal expansion mismatches during joining or assembly with other materials, resulting in stresses at the joints.
Deformability
During the molding process of PPS plastics, slow cooling rates can easily lead to high crystallinity, increasing material rigidity but also reducing strength and impact toughness. This deformability may affect dimensional stability of PPS products.
Environmental impact
PPS plastics typically use petroleum-based carbon fillers, which may have certain negative environmental impacts. Exploring the use of bio-based carbon fillers has become an important development direction.

Although PTFE and PPS have some overlapping applications as high-temperature plastics, there are certain differences in mechanical properties, heat properties, dimensional stability and other aspects. The suitable material should be selected according to actual usage conditions and performance requirements.
Density
The density of PTFE is 2.1-2.3 g/cm³, while the density of PPS is 1.34-1.45 g/cm³. This means that PPS products will be lighter.
Molecular structure
PTFE is made of tetrafluoroethylene monomer polymerization, has a very stable carbon-fluorine bond, which makes PTFE has a very high chemical stability and non-adhesive, PPS by the benzene ring and sulfur atoms alternately connected to the composition of a crystalline polymer, has good thermal stability and mechanical properties. The two differ in molecular structure, which also contributes to the difference in properties.
Heat resistance
PTFE has better heat resistance than PPS. The long-term usage temperature of PTFE can reach 260°C and it can withstand even higher instant temperatures. PPS has a long-term usage temperature up to 220°C and can withstand higher temperatures for short periods. PTFE has better heat resistance comparatively.
Mechanical properties
PPS has higher compressive strength (95-160 MPa), bending strength (120-190 MPa) and elastic modulus (13-17 GPa), while PTFE’s mechanical properties are relatively weaker. This makes PPS more suitable for applications requiring higher mechanical stresses.
Dimensional stability
PTFE has a higher linear expansion coefficient (110-120 μm/m·K) and is more prone to large dimensional changes with temperature variations. PPS has a lower linear expansion coefficient (20-45 μm/m·K) and more stable dimensions. This makes PPS more suitable for applications requiring high dimensional accuracy.
Electrical insulation performance
PTFE has extremely high electrical insulation performance that is hardly affected by temperature and frequency. PPS also has good electrical insulation but is slightly inferior to PTFE, though it maintains relatively good electrical properties even at high temperatures.
Processability
Due to its non-stickiness and high melting point, PTFE is more difficult to process and usually requires special methods like cold pressing and sintering. PPS has better processability and can be molded through conventional plastic processing methods like injection molding and extrusion.
Cost
PTFE’s special molecular structure and processing difficulties make its cost very high. Although PPS is also a high-performance plastic, compared with PTFE its cost is lower and it is more economical and practical.

PPA and PPS in the chemical structure, mechanical properties and application areas, there are significant differences. These differences make them in different application scenarios have their own advantages, can be selected according to specific needs. In actual application, according to the use of the environment, performance requirements and cost and other factors to consider, choose the most suitable plastic material.
Density
PPS is slightly heavier than PPA. PPA’s density is around 1.1 g/cm³, while PPS’ density ranges from 1.34-1.45 g/cm³.
Molecular structure
Their molecular structures are different, resulting in similarities and differences in properties. PPA is composed of polyamide monomers, and the amide groups (-CONH-) in its molecular chains provide good flexibility and toughness. While PPS is formed by alternating connection of phenyl and sulfur atoms to constitute a linear or branched polymer, having highly heat stability and chemical stability.
Heat resistance
PPS has better heat resistance at high temperatures. PPS’ heat deformation temperature (at a pressure of 1.82 MPa) can reach 130-260°C, while PPA is only 120°C. This indicates that PPS can be used in higher temperature environments.
Dimensional stability
PPS has a lower linear expansion coefficient (20-45 μm/m·K) and more stable dimensions, while PPA’s linear expansion coefficient is higher (110 μm/m·K) and is more prone to larger dimensional changes with temperature variations. This makes PPS plastic more suitable for making plastic products with tight tolerances.
Chemical resistance
Both materials have good chemical resistance, but PPS’ chemical stability is slightly better than PPA. PPA has good resistance to most inorganic acids, bases and salts, but poorer resistance to some organic solvents. While PPS has excellent corrosion resistance to a wide range of chemicals including inorganic acids, bases, salts and most organic solvents.
Mechanical properties
PPS has superior mechanical properties. The flexural strength (120-190 MPa) and elastic modulus (13-17 GPa) of PPS are significantly higher than that of PPA (bending strength 110 MPa, elastic modulus 2.4 GPa). This makes PPS more suitable for applications requiring higher mechanical stresses.
Processability
Both PPA and PPS can be processed through molding and extrusion molding. But PPS has a higher melting point requiring special processing equipment and techniques, which increases costs while also posing higher molding challenges for PPS plastics.
Electrical insulation
PPS has better electrical insulation than PPA. PPS can also maintain good electrical insulation properties in high temperature and humid environments. PPA is a member of the nylon family and has good electrical insulation in dry conditions, but its performance decreases after water absorption.
Applications
Their applications differ. PPA is mainly used for automotive parts, mechanical parts, pumps and valves, especially in applications requiring long-term resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion. While PPS plastics are widely used in electronics, aerospace, chemical equipment and other fields, especially in high temperature, high humidity and highly corrosive environments.
Cost
The raw material and processing costs of PPS plastic parts are higher than PPA.
Attractive Plastics is an one-stop plastic injection molder and plastic mold maker that can turn your concepts into real products. For PPS injection molding, we have over 10 years of unique experience. With our knowledge reservoir of engineers and professional management, we can provide comprehensive solutions for high temperature mold making, high temperature plastic injection molding. If you have any challenging plastic molding, complex structured plastic products, please feel free to contact us at any time. we will share our insights and experience with you without reservation.
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) plastics occupy an important position in industrial materials for their reliability and durability in harsh environments. Although its processing cost is higher than regular plastics, its excellent performance and ease of processing make it the first choice for high-performance plastics. With the advancement of technology and the development of new applications, the market prospect of PPS plastics is broad.
Why Choose PPS plastic?
PPS plastic is an ideal plastic material for applications in many industries, especially where parts are used in harsh environments such as high temperatures and high humidity. The reason for choosing PPS plastic is mainly due to its excellent heat resistance, mechanical strength, chemical stability and electrical properties and cost control.PPS plastic can maintain stable performance in high temperature environment, and has good abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance, which makes it in the automotive, electronics, electrical appliances and other fields have been widely used. At the same time, PPS plastic processing performance is excellent, can be molded by injection molding, extrusion and other ways to molding, high production efficiency and stable product quality.












