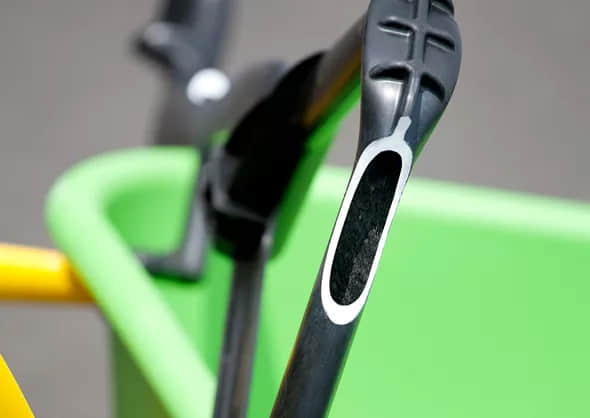

 Increased Strength & Rigidity
Increased Strength & Rigidity
 Reduced Cost
Reduced Cost
 Improved Appearance
Improved Appearance
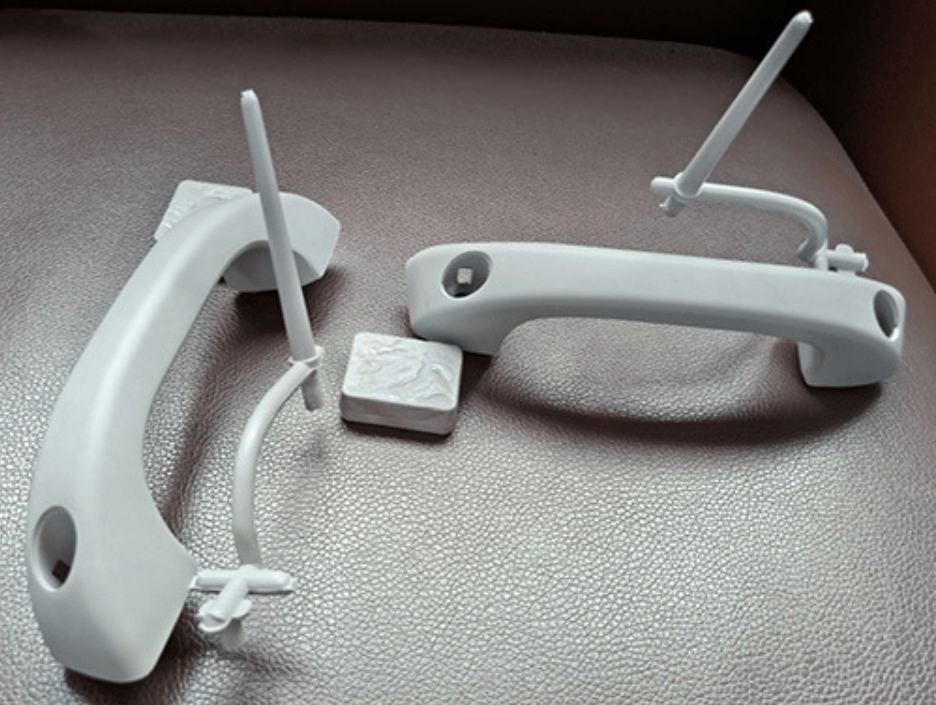
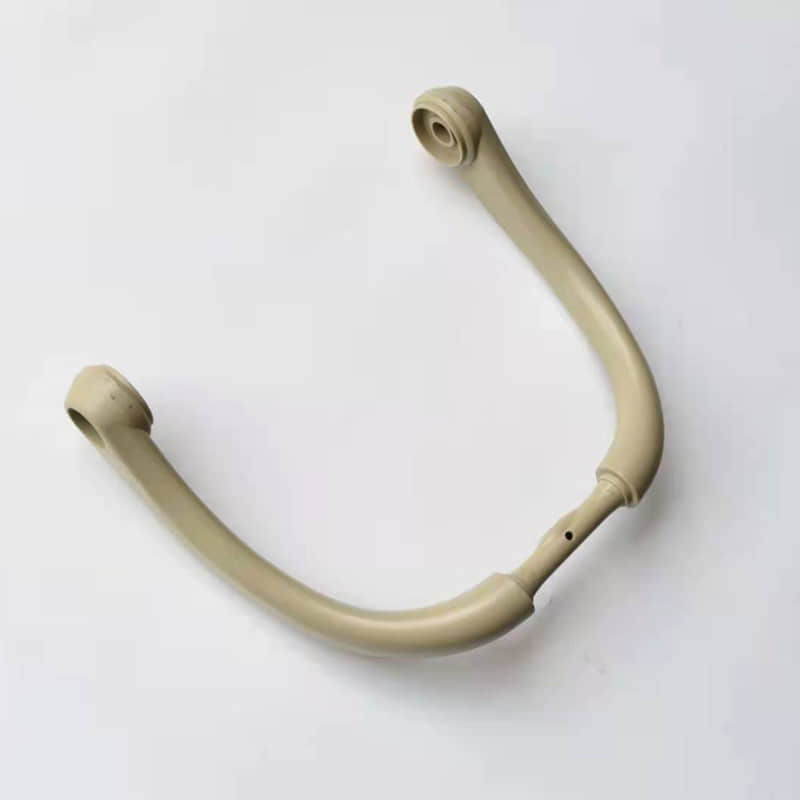
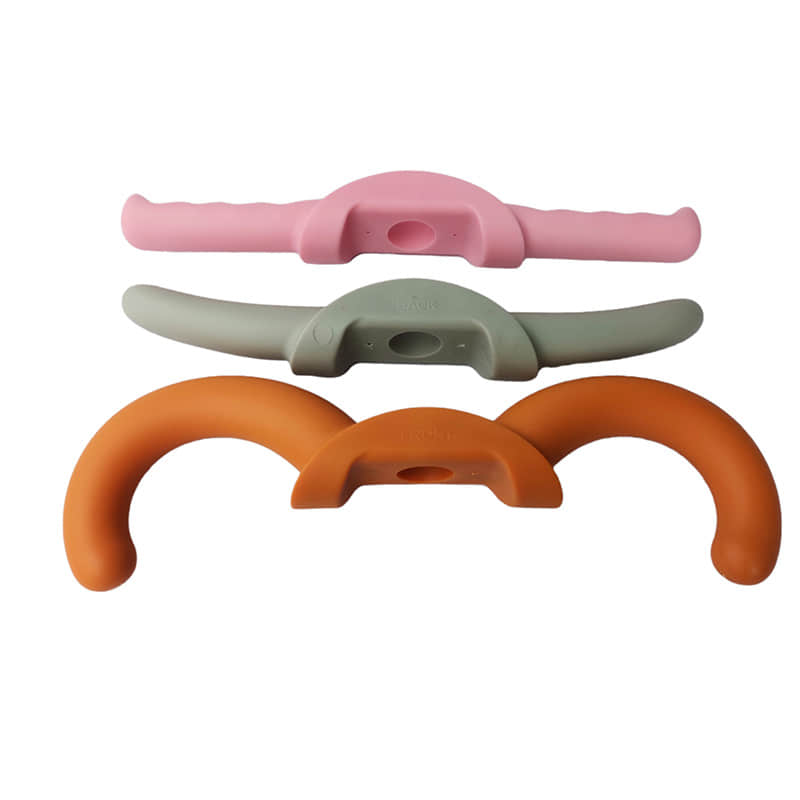
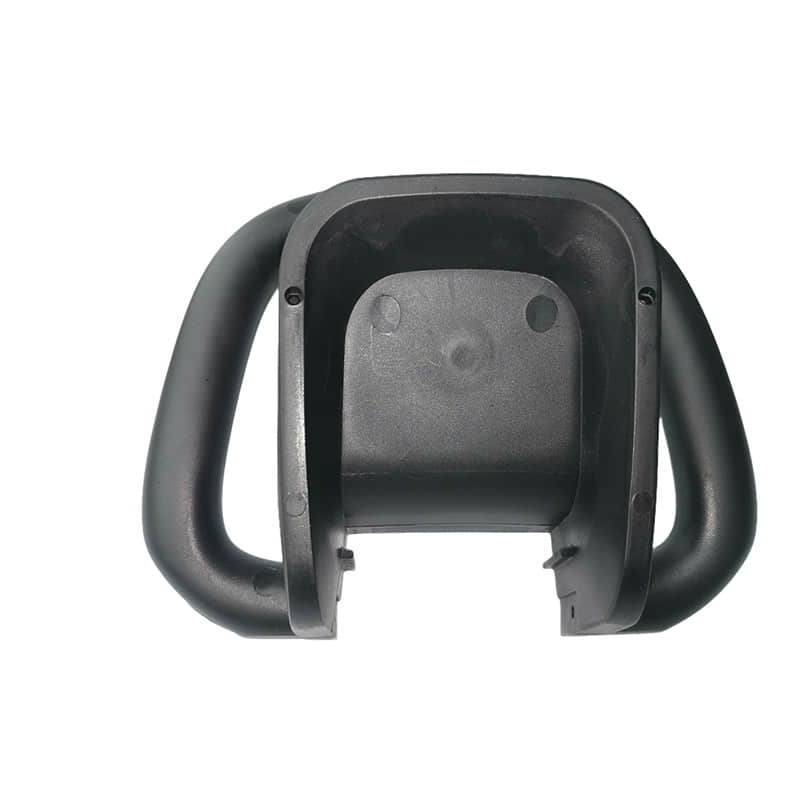
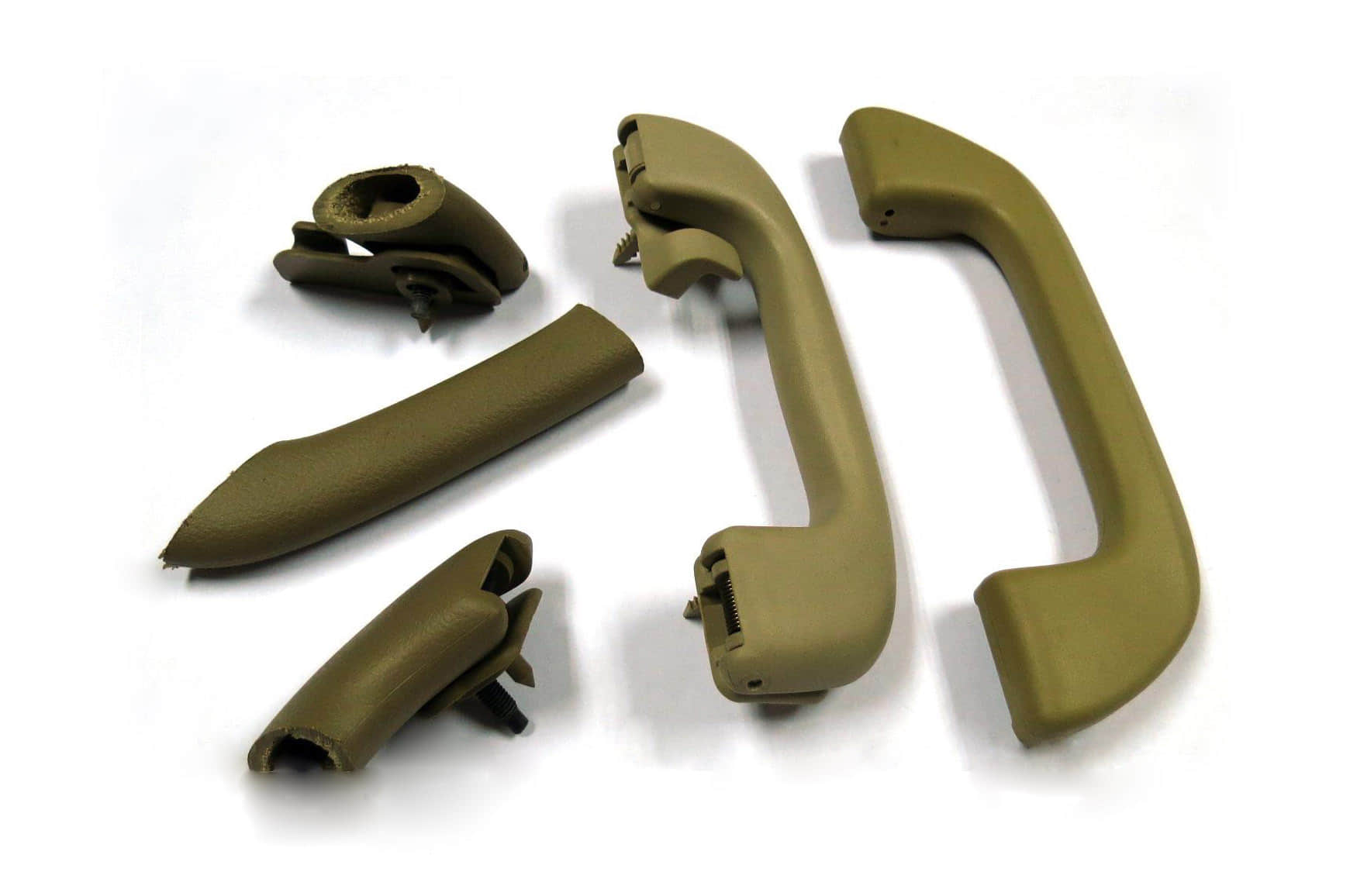
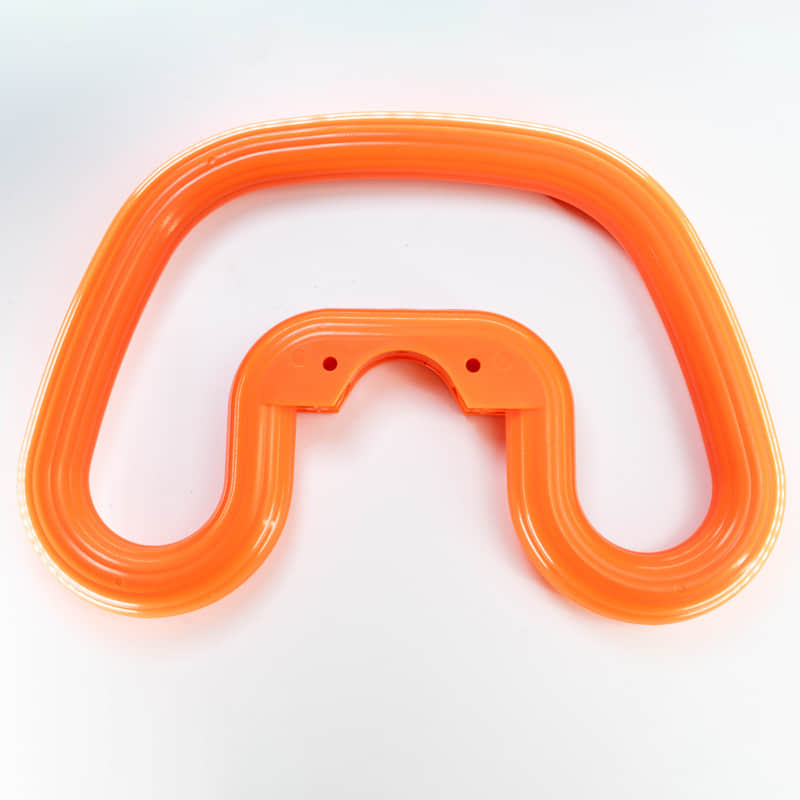
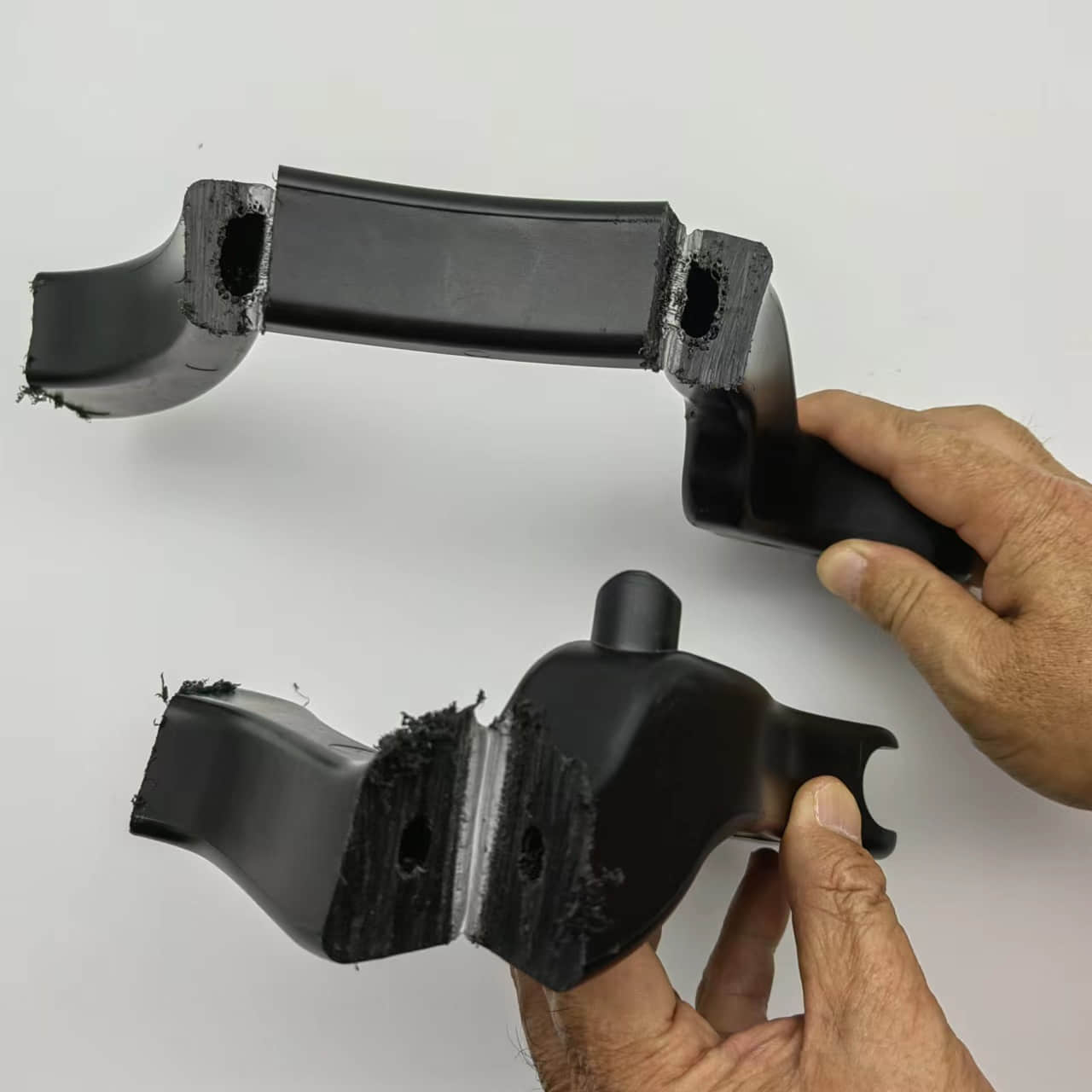




















Gas assisted molding is an injection molding process that utilizes the injection of pressurized gas into the mold cavity to create hollow interior cavities within plastic parts. This specialized process enables the production of lightweight, rigid, and dimensionally stable injection molded parts with thick walls and hollow sections. Gas assisted injection molding requires specialized equipment like gas injection needles and is commonly used to manufacture automotive, medical, and consumer product parts with weight reduction, sink elimination, and material savings benefits compared to solid plastic parts.
The advantages of gas-assisted injection molding are as follows
Gas-assisted injection molding is a specialized injection molding process that involves injecting pressurized gas into the molten plastic in the mold cavity to create hollow interior channels or cavities within the part. The typical process consists of these key steps:
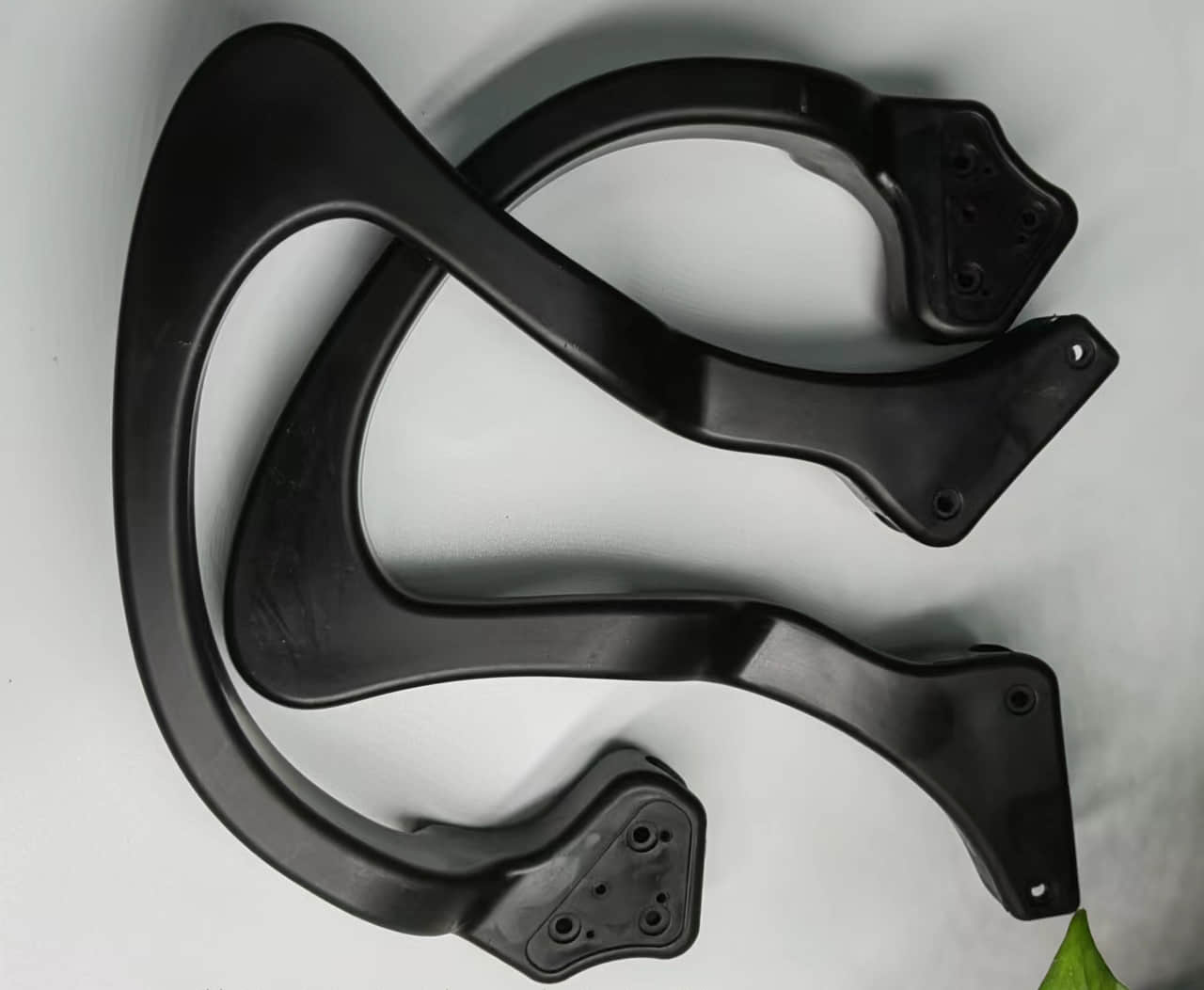
The hollow sections formed by the gas reduce the weight of the part and lower material costs. The gas pressure also minimizes part warpage and shrinkage. This allows the production of large,hollow plastic components with premium surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
The gas assisted injection molding material must allow proper gas penetration and distribution in the mold. The melt viscosity, gas solubility, and rate of crystallization are important factors. Amorphous thermoplastics have molecules that resist gas diffusion and are best suited for gas-assisted molding.
The most common materials used for gas-assisted injection molding are:
Polyethylene (PE) – Popular for large parts like automotive bumpers and industrial containers due to its low cost, chemical resistance, and ease of molding.
Polypropylene (PP) – Used for consumer products, appliances, medical devices. Offers high strength, stiffness, and heat resistance.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) – Provides good stiffness, dimensional stability, and ability to be plated or painted. Used for automotive, electronics, and appliance housings.
Polycarbonate (PC) – Chosen when high strength and heat resistance are needed. Used for medical components, electronic enclosures.
Nylon – Offers a good balance of strength, durability, and chemical resistance. Used for automotive and industrial parts.
PPO – Polyphenylene Oxide: Amorphous plastic with excellent dimensional stability and heat resistance. Common in automotive, electronic housings.
PET – Polyethylene Terephthalate: Extensively used for packaging containers owing to its clarity, strength and barrier properties. Amorphous structure suits gas assist.
PMMA – Polymethyl Methacrylate (Acrylic): Amorphous plastic valued for optical clarity and weather resistance. Used for medical devices, LCD screens.
Depending on the complexity and size of your gas-assisted plastic parts, we will make an overall assessment and respond to you with a reasonable production time, which usually takes 4 to 6 weeks to complete.