





Silk screen, this ancient and dynamic printing process, has gone through a long history of development and still plays an important role in various fields.
In this article, we will delve into the concept, types, process , application fields, etc. of silk screen printing, to help you gain a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of this process.
Screen printing is a printing technique. It is also called silk screen printing, serigraph, silk screening or silk screen printing. It transfers ink or other printing media onto a substrate using a silkscreen as a stencil. Screen printing includes the following: silk screen, squeegee, ink, printing table and substrate. Its printing principle is based on the silkscreen stencil allowing ink to pass through image areas while blocking ink in non-image areas. Silkscreens are typically made of materials such as silk, nylon or stainless steel and contain small holes or meshes. The size and shape of these meshes determine the detail and clarity of the printed image. This technique is widely used on glass, wood, plastics, metals, clothing and is particularly suitable for CNC metal parts and injection molded parts.
Screen printing is a wet-process printing technique where an image is transferred to a substrate through the use of a stencil and a squeegee. It is a form of stencil printing and is one of the four basic printing methods along with relief, intaglio and lithography.
Screen printing has its origins in China over 2000 years ago. During the Qin and Han dynasties, the Chinese began using the reserved printing technique to dye fabrics with carved boards, which can be considered the origin of screen printing.
In the Song dynasty, silkscreen printing techniques developed further. People started using horse hair or human hair to make templates for finer details. The oil-based inks were also improved by adding starch materials to make them into pastes for silkscreen printing, producing prints with richer colors.
In 1907, Samuel Simon of England invented screen printing and applied for a patent. Around 1915, the US first adopted photographic methods to make screen printing stencils, achieving a major breakthrough in its development. Since then, screen printing developed rapidly and was widely applied in various industries.
In the 1950s, with the development of Pop Art and graphic design movements, screen printing became popular in commercial applications. T-shirt and fabric screen printing officially began during this era.
Today, screen printing has become a mature commercial printing process. its suitability for various substrates, screen printing has been applied by industries such as apparel, electronics manufacturing, metals, plastics and more. The introduction of digital technologies has further promoted the development of the industry.
When conducting screen printing, ink selection, control of printing pressure and substrate preparation also need attention in order to achieve optimal print results.Here is a breakdown of the screen printing steps:
Before starting screen printing, a design first needs to be created or prepared. This typically involves using graphic design software to create vector graphics or bitmap images, ensuring the design’s resolution and clarity is suitable for printing. Considerations should be made regarding the technical limitations and requirements of screen printing, such as line thickness, number of colors, etc. After completion, the design needs to be output onto a transparent film or plate suitable for screen printing.
The screen is a crucial part of screen printing and its quality directly impacts the print quality. Select a suitable screen mesh material like polyester fibers (nylon) or nylon based on printing requirements. The size and shape of the mesh will affect print details and quality. The screen needs to be tightly stretched on the screen frame to ensure it is flat and wrinkle-free. Screen frames are usually made of aluminum alloy to secure the screen and facilitate operation.
Place the screen on a coating machine and apply a layer of photosensitive emulsion. This emulsion will harden and become insoluble through a chemical reaction under specific light. Then place the previously prepared design film on the emulsion coated screen and expose it using a UV light exposure unit. During exposure, UV light passes through the transparent areas of the film, causing the emulsion to harden through polymerization and forming a pattern corresponding to the design. Separate screens must be created for each color if it’s a multi-color print.
After exposure, wash the screen under running water. The unexposed emulsion will be rinsed away while the exposed emulsion remains on the screen to create a stencil.
After washing, the screen needs to air dry to ensure the emulsion stencil fully cures. Sometimes the stencil may require inspection and touch-ups to ensure printing accuracy and completeness. The screen needs to be remade if the quality is poor.
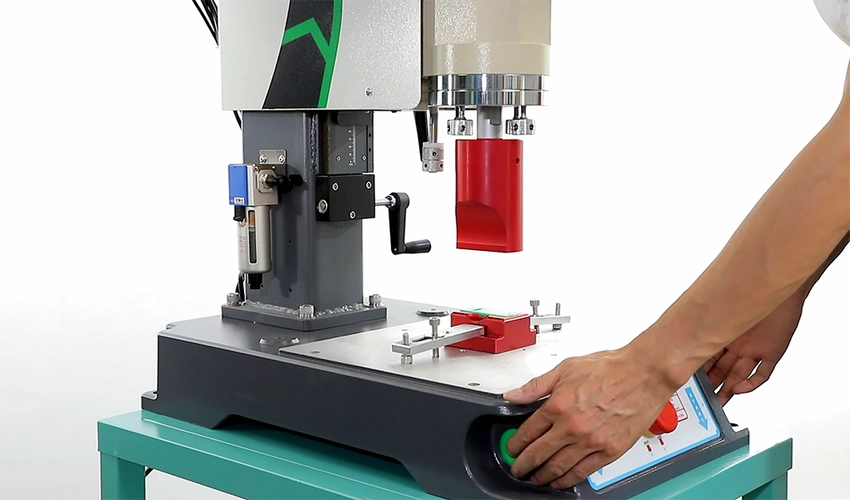
Place the substrate to be printed (e.g. paper, fabric) on the printing table and register the screen frame over the print location. Ink is applied on the stencil areas of the screen then scraped evenly across using a squeegee blade. Ink adheres to the substrate through the open areas where emulsion has been washed away, forming the desired image. This process can be done manually or using mechanical printing equipment.
After printing, drying is required to cure the ink firmly onto the substrate. Inspection is also needed to ensure print quality meets requirements without issues like smudging, missing prints or accurate color reproduction. Finally, finishing touches like organization and packaging of prints are completed to prepare for delivery or further processing.
Choosing a right screen printing process is crucial for achieving design effects and meeting customer needs. In practice, the specific printing requirements and conditions need to be considered for selection.
Duotone screen printing is a process using two ink colors to print images. It controls the mix ratio of the two inks to achieve different tones and color effects. Duotone is commonly used for artworks and posters. Compared to single color printing it offers stronger color expression but precision cannot match four color printing.

Spot color screen printing refers to printing a single color ink through a screen onto the substrate. It is typically used for simple graphics, text or logos. Features of spot color screen printing include accurate color reproduction with pure, saturated colors matching the designer’s intent. As only one color is used, the stencil making process is relatively simple and cost is lower.
Halftone screen printing simulates a continuous tone image through arrangement of dots. During printing, dots of varying sizes and density distributions are used to render tonal gradations from light to dark visually presenting a continuous tone. This process is commonly used for photo and graduated background images requiring continuous tone. It enables richer color blending but stencil making is relatively complex requiring precise dot size and distribution control.
Grayscale screen printing uses different shades of gray to represent the lightness levels of an image. It achieves smooth transition from black to white to print images with a gray tone effect. Grayscale is often used for reproducing photographs and artworks. It implements refined color expression but requires more screens and assembly, increasing costs.
CMYK four color screen printing uses cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks to print color images by controlling the mix ratio of the four inks to produce various colors. As four colors are used, stencil making is more complex but enables high quality color printing, currently the best commercial process. However, four screens are needed, increasing costs and difficulty.

Simulated process screen printing mimics effects of traditional print processes using special inks and techniques. It can simulate etchings, relief and intaglio printing effects. This creates unique textures and qualities for an artistic personalized finish. Special stencil techniques and processes are usually required, increasing costs but satisfying some niche design requirements.
Screen printing requires a variety of tools and equipment to complete this simple yet complex process. Now let us understand the main equipment. Now let’s understand the role they play in the printing process.
The screen printing machine is the core equipment in the screen printing process used to print ink onto materials through a stencil screen. A screen printing machine generally consists of a frame, screen clamping device, squeegee system and printing table. The frame provides the structural support as the backbone of the whole machine, ensuring stability and precision during printing. The screen clamping device fixes the screen to maintain its position stability during printing. The squeegee system evenly pushes ink through the screen using a squeegee so that the ink adheres onto the material through the screen’s open areas. The printing table is used to place and secure the substrate being printed.

Ink is an indispensable material in screen printing used to form the final print pattern. Different ink types can be selected such as water-based ink, oil-based ink and UV ink depending on the printing material and effect requirements. The color and quality of ink directly impact the visual effect and quality of prints. Ink selection should consider the material of the substrate as well as the intended effects, mainly in terms of adhesion, drying speed, light fastness to ensure the prints have good durability and stability.
The screen is a key component in the screen printing process serving as the medium for ink transfer. The screen quality and selection are critically important to the print outcome. Parameters like material, mesh size, thread counts all affect ink pheremetry and print pattern precision. Different screen mesh materials and sizes are suitable for different print jobs. Common screen materials include polyester fibers and nylon which have good elasticity and abrasion resistance for long term use. Different specification screens can be chosen according to printing requirements for optimal results.
The squeegee is used to push ink through the screen mesh onto the substrate. Its shape and hardness affect the print results such as ink thickness and uniformity. Common squeegee materials include rubber and polyurethane with good elasticity and abrasion resistance. The shape can be customized as needed to suit different screen mesh structures and printing requirements.
The dryer is equipment used to accelerate the ink drying process through heated air or radiant heat. Dryers typically consist of a conveyor belt, heating system and blower. Dryers can effectively improve print drying speed and quality.
Ink may remain on the screen or equipment during printing, affecting subsequent prints. Therefore, regular cleaning of screens and equipment is needed to maintain them in good working condition. Washout stations generally include washing tanks, cleaner and washing tools. Timely cleaning can extend the lifespan and improve efficiency and quality.
There are many materials suitable for screen printing. Here are some common materials:
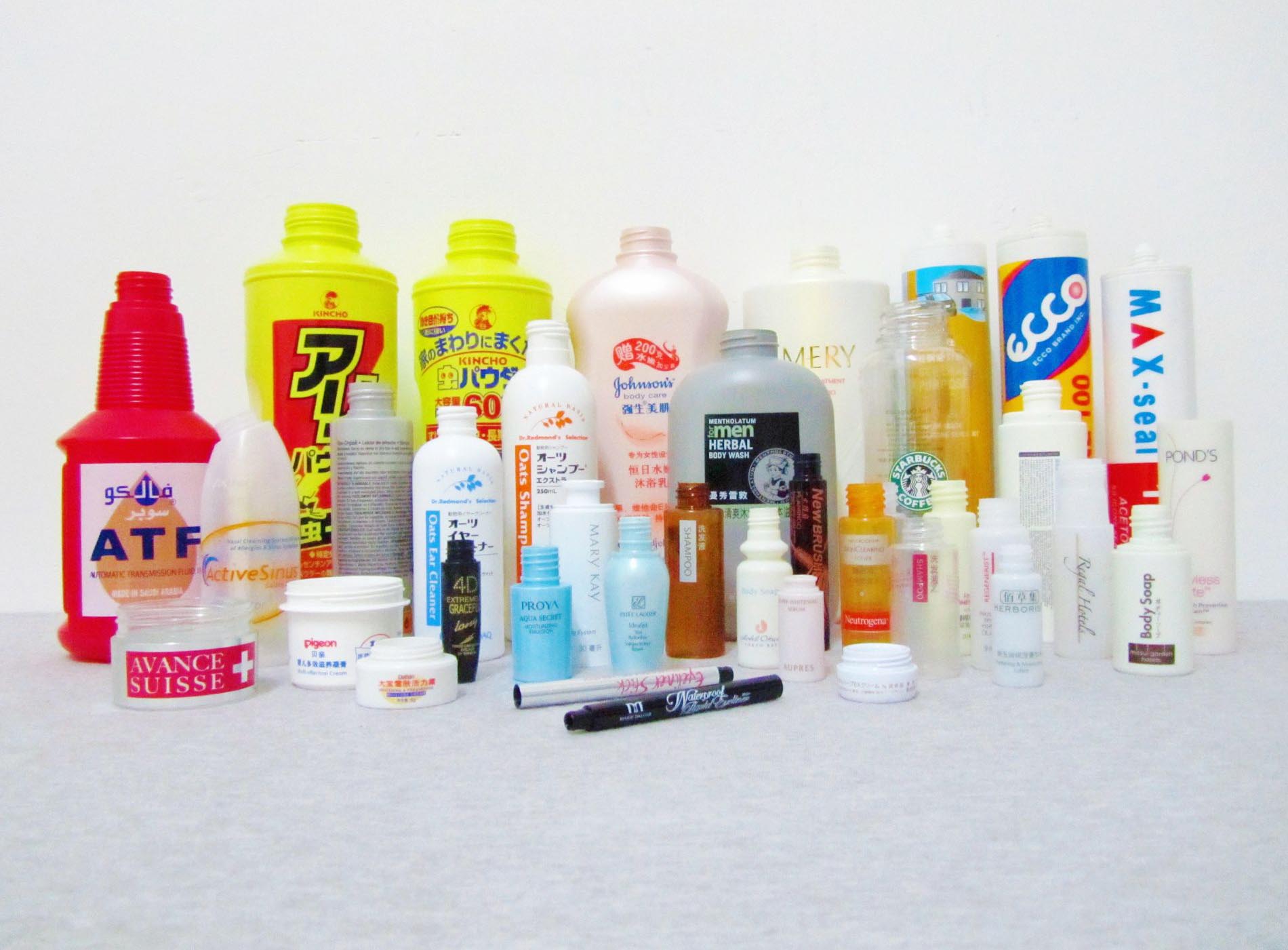
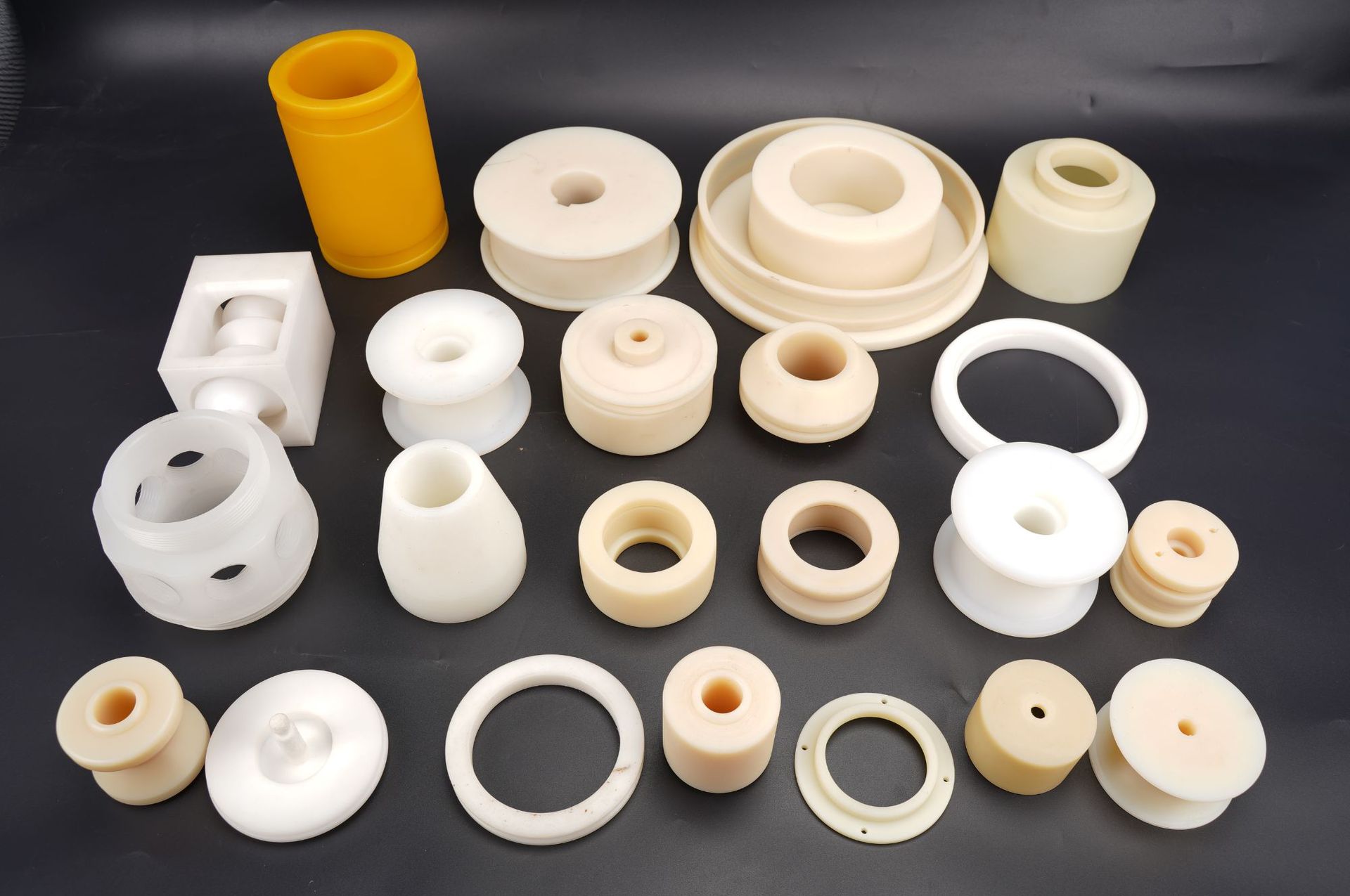
Plastic is one of the most commonly used substrates for screen printing ink. Common plastics like ABS, PP, PS, SAN, PC, Nylon, etc. are suitable for screen printing. Different plastic substrates require using screen inks to ensure good adhesion and stretchability.
However, based on our 20 years of experience in silk screen printing, some materials don’t adhere well during printing and require special pretreatment before printing. For example, with PP plastic, the industry practice is to pre-burn it with heat before printing to ensure adhesion. HDPE has very poor adhesion and is not suitable for printing. ABS doesn’t require any pretreatment – it prints with excellent quality

Metal substrates are also a primary type suitable for screen printing ink. Metals have good conductivity and reflectivity, making patterns screen printed on metals appear more vivid and aesthetic.
Glass substrate has a relatively special application in screen printing ink. Graphic patterns can be printed or coated on glass to produce various decorative and craft glass products.
Wood surface is also suitable for screen printing to create products with unique textures and color effects.
The clothing industry widely uses silk screen printing technology to print logos, especially T-shirts, hats, towels, etc.
Paper and other paper materials are also common substrates used for producing prints like posters and pamphlets.
![]()
Silicone and rubber materials are also suitable for silkscreen printing, but the adhesion strength needs consideration during printing. They can be baked at 150°C for 30 minutes to increase adhesion strength in such an environment.
Other materials like leather, crystal, ceramics are also suitable for screen printing applications to manufacture products with distinct textures and aesthetics, meeting various industry demands.
It’s worth noting that different materials require using different inks and printing processes to ensure print quality and effects.
Screen printing is an efficient printing process that enhances brand and product recognition. Here are some of the key benefits of screen printing:
Screen printing can be applied to many materials such as metal, plastic, ceramics, glass, etc. This provides wide application across various fields. Additionally, it can print not just on flat surfaces but also on objects with special shapes like curved surfaces, thus fulfilling the printing needs of parts with varied shapes.
Screen printing can achieve high quality print effects with vibrant colors, sharp patterns and strong sense of layers to meet users’ visual effect requirements.
The patterns printed through screen printing process have strong durability as the inks and pigments are resistant to fading, peeling or loss over long term use and friction, keeping an aesthetic appearance for a long time.
Compared with other printing technologies, screen printing has higher efficiency to quickly print large volumes of products, suitable for mass production.
Screen printing has a relatively low cost, especially suitable for short-run and customized printing needs.
Screen printing allows the use of multiple colored inks to achieve rich color effects. For multi-colored printing, each color can be printed separately to maintain the most authentic shades.
As the ink passes through the screen mesh pores onto the substrate, the amount of ink left on the surface can be controlled. The more ink remaining, the stronger the sense of layers and unique charm for the product, also increasing competitiveness.
Although screen printing has its unique advantages, it also has some disadvantages that can’t be ignored. Here are some of its main disadvantages:
Compared to digital printing or relief printing, the precision of screen printing is slightly inferior. It may not be able to accurately replicate extremely fine patterns or text, which could cause issues in applications requiring high precision.
Screen printing requires making customized screens, especially for complex patterns or multiple colors, which often necessitates multiple print runs. This not only increases production costs but the overall process is relatively elaborate and may require more time and labor.
Screen printing’s color performance is constrained by screen counts and ink types. While it can print rich colors, some specific color effects or multicolor printing may be difficult to achieve.
Chemicals like inks and solvents used in screen printing can pollute the environment. Improper management may result in harmful emissions threatening the ecology, environment and human health.
Screen printing often has difficulty achieving ideal gradient or halftone photographic effects due to limitations in printing principle. It may not be able to accurately replicate continuous tone changes.
Given its relative simplicity and common use for printing identification marks, screen printing can adapt to various application scenarios.
Screen printing plays a key role in the manufacturing of electronic and electrical products. For example, it is used to print circuits, connections and other necessary patterns and identification on circuit boards. It can also be used to print other electronic components such as circuit boards, displays, touch screens, etc.
Screen printing technology is also widely used in manufacturing medical devices. Identifying and labeling medical equipment, printing circuits boards, medical sensors and biosensors are specific applications in this field.

Many toys like Lego bricks, game boards, trading cards are made through screen printing.
Printing in clothing and textiles is basically accomplished through screen printing, such as printing clothes, shoes, handbags, etc.
Applications in advertising include producing billboards, signs, banners, posters as indoor and outdoor media. It is also widely used for trademark printing to strongly promote brands.
In packaging, screen printing is used to print logos, barcodes, patterns and text on packaging boxes, bags, bottles to provide attractive packaging and necessary product information labeling.
Screen printing technology can print wallpaper, carpets, curtains and other home decor items to add color and personalized touches to living spaces.
Screen printing is widely used for printing patterns and identification on vehicle bodies as well as identification on automotive parts to provide aesthetic appearance and necessary vehicle information.
Screen printing and pad printing each have their own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a printing process, the correct printing solution should be selected based on the product shape, quantity, quality requirements, etc.
Screen printing involves transferring ink through the mesh openings of a screen to form patterns on the product. This process requires tools like screens, inks, rolls, and special equipment for curved surfaces. Pad printing uses a silicone pad to transfer printed ink from patterns on a metal plate onto a workpiece, similar to stamping. Its printing is limited by pad performance and shape.
Screen printing printing area is basically unlimited, screen costs are low and they can be reused. It suits flat and curved surface printing but requires a regular flat or curved surface within certain printing ranges. Pad printing can print on any surface including flat, curved, wavy, with no shape limitations, though printing area is limited.
Screen ink layers are thicker for strong dimensionality and color expression but multi-color overlay adds challenge. Pad inks layers are thinner but allow color overlays on any surface, demonstrating excellent color expression and adaptability, called “universal printing”.
Screen printing suits high-end surface printing due to its dimensionality and color expression, e.g. imitation prints and oil painting copies. Pad inks are thinner with slightly weaker visual effects.
Pad printing can usually achieve higher precision as each pixel’s position and color can be controlled. Screen precision is relatively lower due to screen limitations.
Screen printing suits various materials like paper, plastic, metal. Pad printing usually suits flat and curved materials like plastic, glass, ceramics.
Screen printing costs are relatively lower especially for mass production. Pad printing costs are somewhat higher.
Screen printing and digital printing each have their own advantages and disadvantages, suitable for different application scenarios and demands. When choosing a printing technique, specific conditions need considering.

Screen printing is suitable for printing various materials like paper, plastic, metal, etc. Digital printing is generally suitable for paper and some special materials.
In some cases, screen printing may be less environmentally friendly, e.g. its water washing process could cause environmental issues and its environmental costs are relatively higher. Digital printing has an advantage in this regard as it uses environmentally friendly textile inks meeting modern green requirements.
Screen printing uses a screen to transfer ink or other coatings onto the substrate. Digital printing directly prints computer files onto the medium without plate-making, using CMYK primary colors printed by digital inkjet heads mixing various colors according to each color’s proportion.
Digital printing can generally achieve higher printing precision as it can control the printing position and color of each pixel. Screen printing precision is relatively lower as it is limited by the screen.
Digital printing usually allows faster printing speed as it can print large amounts of images quickly. Screen printing speed is relatively slower as it requires individual screens for printing.
Screen printing cost is relatively lower, especially for mass production. Digital printing cost is relatively higher, especially for short runs.
Whether screen printing ink can be washed away depends mainly on the ink material, printed substrate, and cleaning agent and method used.
Firstly, the ink material itself is the key factor in determining its cleanability. Inks of different materials have varying resistance to cleaning agents. Some inks may be more easily dissolved or removed by certain cleaning agents while others may require more forceful cleaning methods.
Secondly, the printed substrate also affects ink cleanability. Different substrates have varying ink adsorption capabilities, so the substrate’s characteristics need considering to avoid damage during cleaning.
In addition, the cleaning agent and method used are also very important. The cleaning agent and method suitable should be selected based on the ink material and substrate characteristics. Some cleaning agents may contain chemicals that can dissolve the ink, while methods such as spraying, wiping will also affect cleaning effects.
To improve screen printing ink durability, high quality ink can be chosen, and appropriate post-processing and protection conducted according to the printing material and usage environment. For example, a fixation process after printing can enhance ink adhesion and durability.
As an economical, mature and reliable technique, screen printing can print your unique designs on products made of various materials. For those who want to print graphics or logos, screen printing is the ideal choice. In the future, screen printing technology will continue to develop towards higher efficiency, environmental protection and intelligence, bringing more surprises and convenience for people.












